Photoresistors, also known as LDRs (Light Dependent Resistors), are simple, inexpensive, and versatile light sensors. They detect the amount of light in the environment and are perfect for robotics, home automation, and DIY projects.
A photoresistor is an electronic component whose resistance changes based on the light it receives:
When light increases, its resistance decreases.
When light decreases, its resistance increases.
By connecting it to an Arduino through an analog input pin, we can read a numeric value between 0 and 1023 that reflects the light level. This makes it ideal for automatic lighting, light-following robots, ambient light detection, and more.
To build this project, you’ll need:
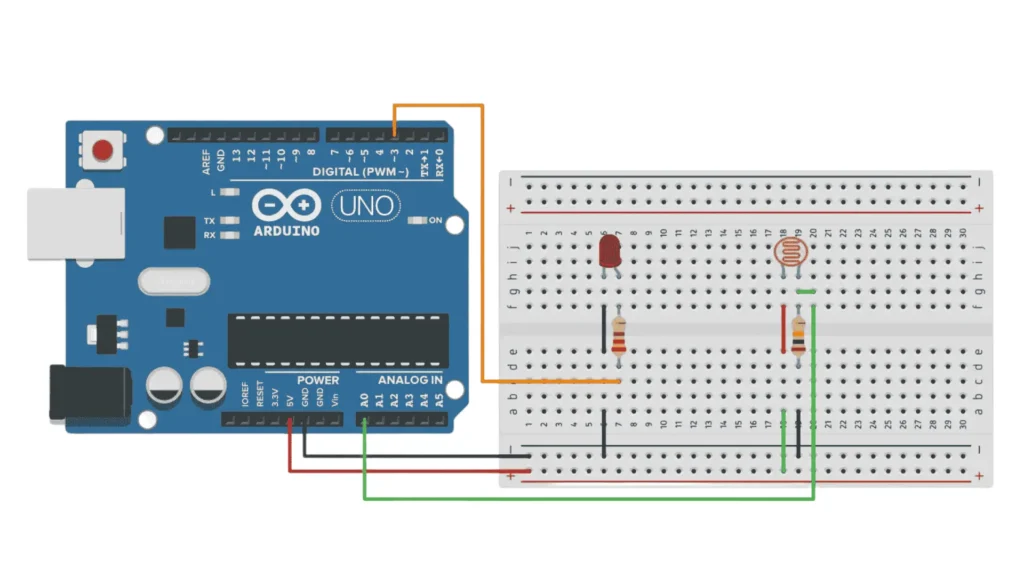
Here’s the code
// Pin definitions
int pinLDR = A0;
int pinLED = 3;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication
pinMode(pinLED, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
int lightValue = analogRead(pinLDR); // Read light level
Serial.println(lightValue); // Print value to Serial Monitor
if (lightValue < 500) { // If light is below threshold
digitalWrite(pinLED, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
} else {
digitalWrite(pinLED, LOW); // Turn off the LED
}
delay(200); // Wait 200 ms
}
Let’s review the code section by section:
We define two variables to associate Arduino pins with the components.
int pinLDR = A0;
int pinLED = 13;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(pinLED, OUTPUT);
}
The setup() function runs once when the Arduino powers up:
Starts serial communication at 9600 baud.
Sets the LED pin as a digital output.
void loop() {
int lightValue = analogRead(pinLDR);
Serial.println(lightValue);
Continuously reads the analog value from pin A0 (0–1023) and prints it to the Serial Monitor.
if (lightValue < 500) {
digitalWrite(pinLED, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(pinLED, LOW);
}
If the light value is below 500 (dark environment), the LED turns on. Otherwise, it stays off.
You can adjust the 500 threshold according to your environment and sensor sensitivity.
delay(200);
}
Pauses the program for 200 milliseconds before repeating the reading and control cycle.
Low values (close to 0): very bright light
High values (close to 1023): low light
The threshold value of 500 can be changed to suit your needs.
Assemble your robot and get started to learn Robotics!