Servo motors are widely used in robotics, automation, and RC models because they can move to specific angles with precision. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to connect a servo motor to an Arduino Uno and control its position with simple code.
1× Arduino Uno
1× Servo Motor (like SG90 or MG90S)
3× Male-to-male jumper wires
1× USB cable for Arduino
A servo motor is a small device that can rotate to a specific position and hold it there. It’s different from a regular DC motor, which spins continuously, because a servo moves to a precise angle based on the signal it receives. This makes it perfect for projects where you need accurate control, like moving the arm of a robot or steering a small vehicle.
The servo receives a control signal through a technique called PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). By changing the width of this signal, you tell the servo which angle to move to — typically between 0° and 180°. Inside, the servo has a small motor and a control circuit that interprets the signal and adjusts the position accordingly. Thanks to Arduino’s built-in Servo library, you don’t have to manage these signals manually: you simply tell the servo the angle you want, and the library does the rest.
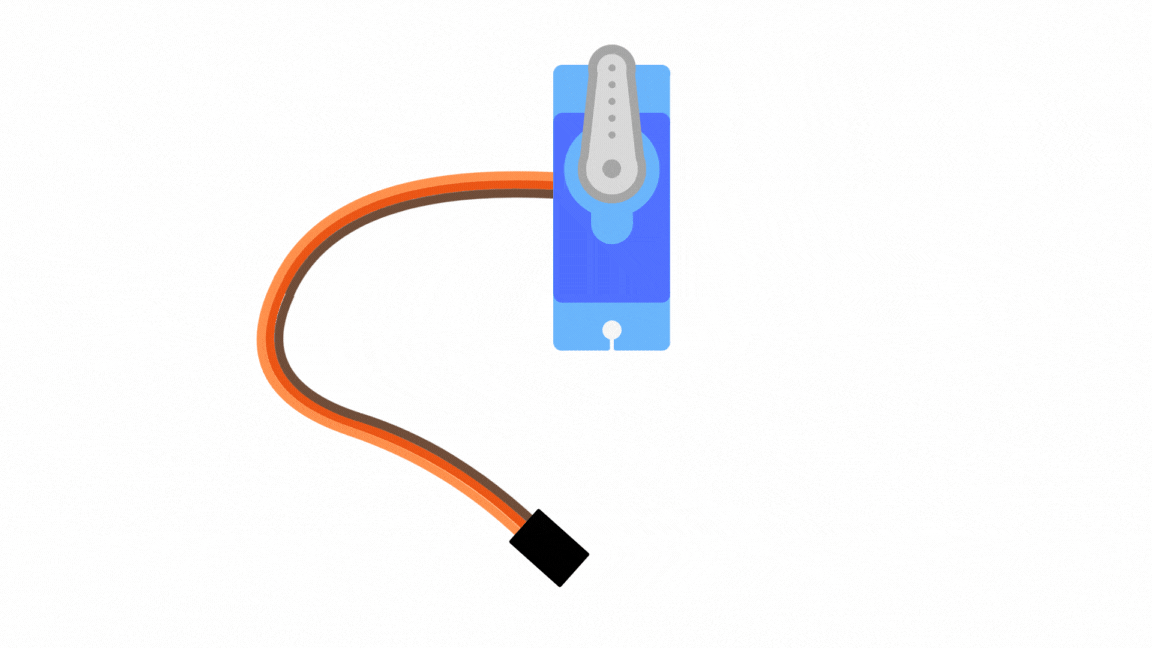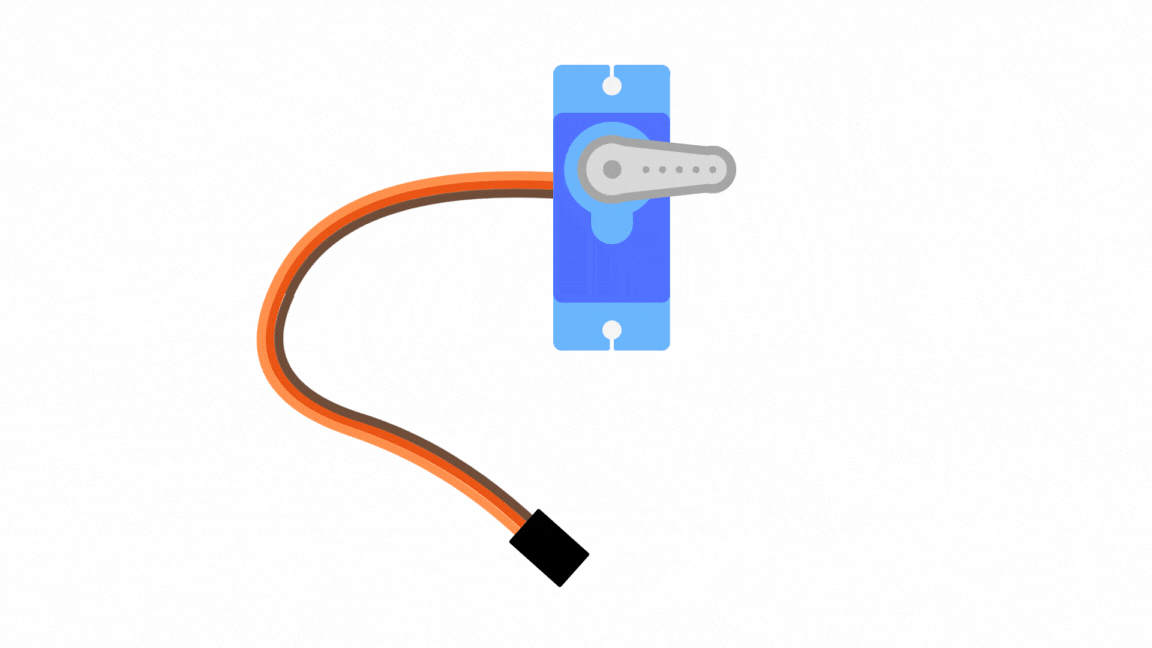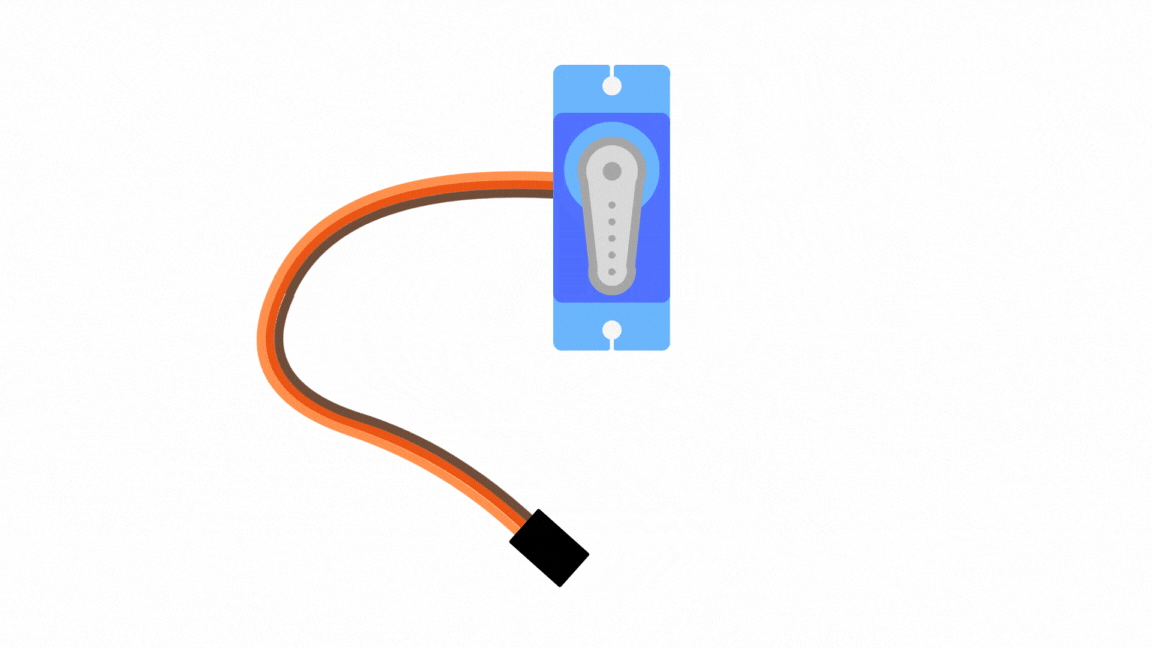
| Servo Wire | Arduino Uno |
|---|---|
| Brown/Black (GND) | GND |
| Red (+5V) | 5V |
| Orange/Yellow (Signal) | Digital pin 9 |
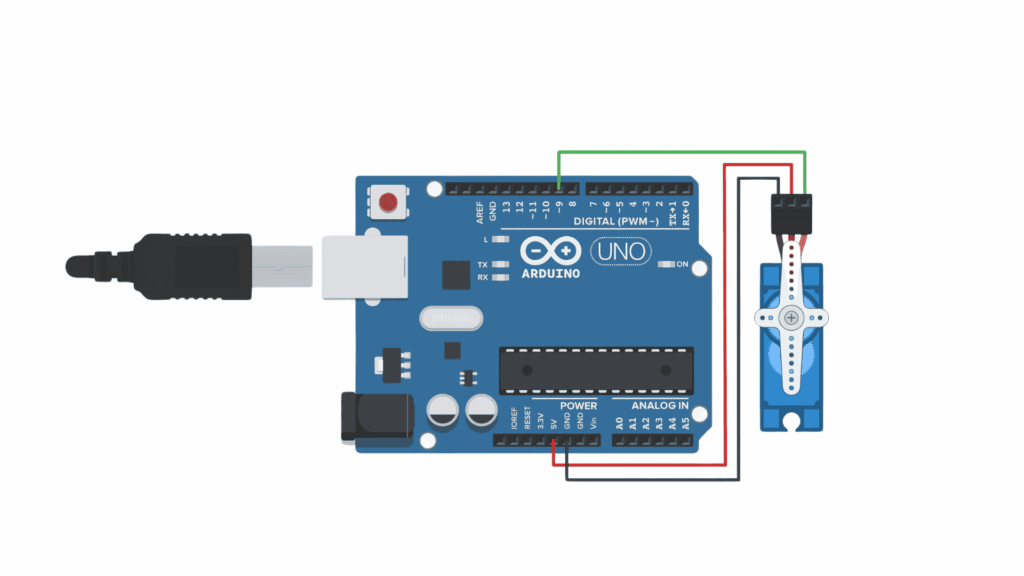
We’ll use the built-in Servo library in Arduino IDE to make it easier to control the motor.
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library
Servo ServoMotor; // Create a Servo object
void setup() {
ServoMotor.attach(9); // Attach the servo to digital pin 9
}
void loop() {
ServoMotor.write(0); // Move to 0 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second
ServoMotor.write(90); // Move to 90 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second
ServoMotor.write(180); // Move to 180 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second
}
Let’s review the code section by section:
Adds the Servo library, providing functions to control servo motors.
#include <Servo.h>
Servo ServoMotor;
Creates a Servo object named ServoMotor to control the motor.
void setup() {
ServoMotor.attach(9);
}
Links the servo motor control wire to digital pin 9.
void loop() {
ServoMotor.write(0);
delay(1000);
ServoMotor.write(90);
delay(1000);
ServoMotor.write(180);
delay(1000);
}
Moves the servo to 0°, waits 1 second
Moves to 90°, waits 1 second
Moves to 180°, waits 1 second
Repeats forever
Connect Arduino Uno to your computer via USB
Open the Arduino IDE
Copy and paste the code
Select Tools > Board > Arduino Uno
Select the correct Port
Click Upload (the right arrow button)
The servo motor should now move between 0°, 90°, and 180°.
Assemble your robot and get started to learn Robotics!