Configuring and Launching Controllers in ROS 2 with ros2_control
When a robotic system starts moving real or simulated actuators, it enters one of the most delicate phases of its entire architecture: control. In ROS 2, this responsibility is handled by ros2_control, a framework designed to manage the interaction between high-level software and hardware in a modular, extensible, and safe way. The goal of ros2_control […]
Managing Parameters in ROS 2: Dynamic Node Configuration with Python and CLI
When developing complex robotic systems, one of the most critical requirements is the ability to adapt software behavior without recompiling code. In ROS 2, this goal is achieved through parameters, a fundamental mechanism that enables nodes to be configured dynamically, safely, and flexibly. Parameters make it possible to separate node logic from configuration values. This […]
How to Manage Parameters in ROS 2 Using C++

👩🏻💻 Core Concepts, Practical Implementation, and CLI Tools In ROS 2 development, parameter management is a fundamental capability for building flexible, configurable, and adaptive robotic systems. Any autonomous robot must be able to modify its behavior without recompilation: sensor frequencies, maximum speed, module activation, safety limits, and numerous other factors depend on values that must […]
How to Create and Understand a URDF Model in ROS 2
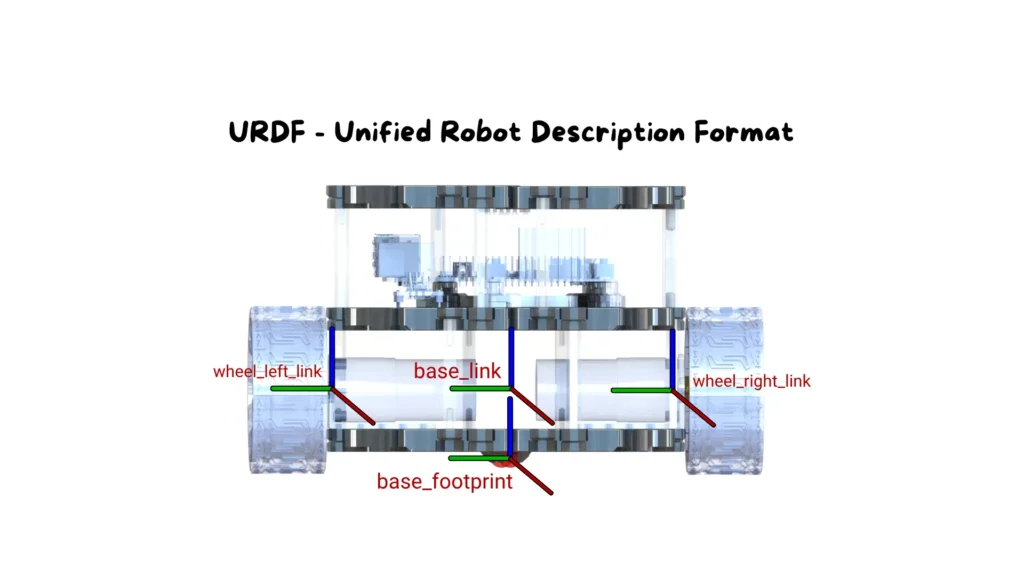
When working with ROS 2, sooner or later you reach the point where you must describe the physical structure of your robot in detail. This is a fundamental requirement: every component of the ROS 2 ecosystem—RViz, Gazebo, Nav2, controllers, planning libraries—needs to know the dimensions, connections, and shape of each element that makes up the […]
Creating and Managing a Lifecycle Node in ROS 2 with C++
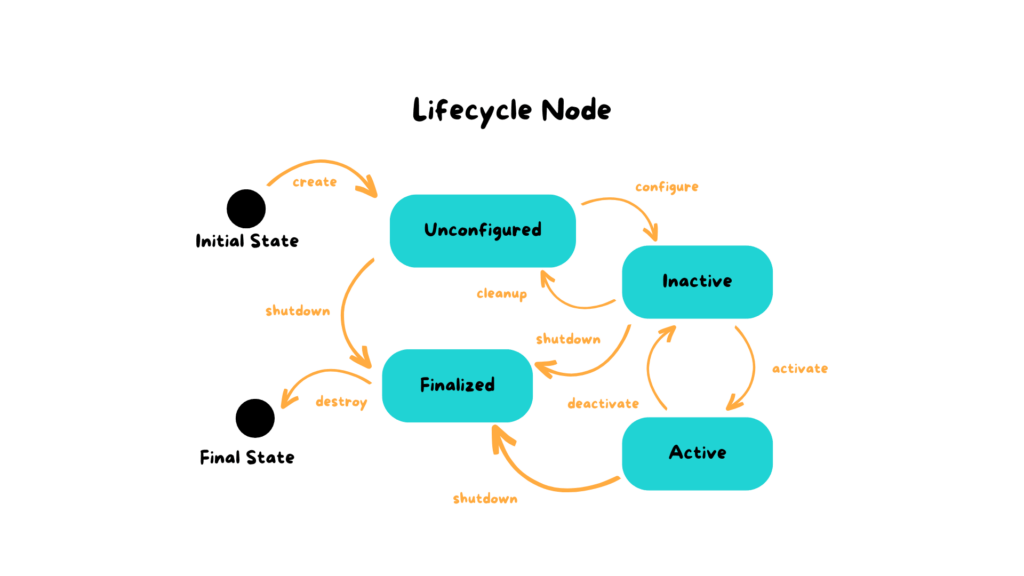
When developing complex robotic systems, managing the operational state of each node precisely is essential to ensure stability, safety, and predictability.ROS 2 introduces a key concept to meet this need: Lifecycle Nodes. Unlike standard nodes, which start operating as soon as they are launched, Lifecycle Nodes allow you to explicitly control their behavior through […]
Managing and Creating Lifecycle Nodes in ROS 2

When developing complex robotic systems, the ability to precisely control the operational state of each node is essential to ensure reliability, safety, and maintainability. ROS 2 addresses this need through a key concept: Lifecycle Nodes.Unlike regular nodes that start operating as soon as they are launched, Lifecycle Nodes allow you to manage their life cycle […]
Mastering Nav2 Costmaps in ROS 2: Static, Obstacle, and Inflation Layers Explained
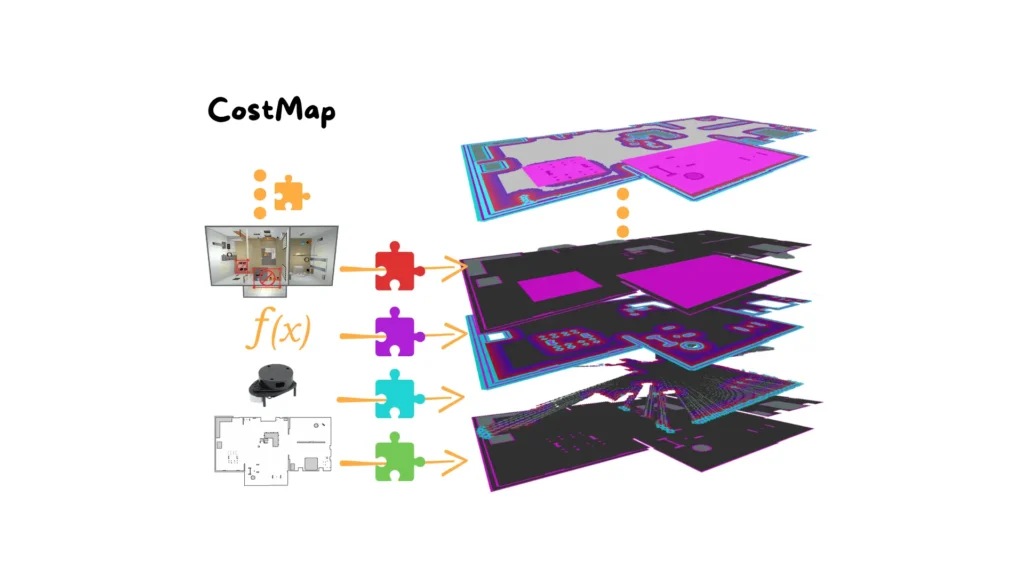
When we move from simple robot experiments to real-world navigation, the environment is no longer an abstract concept. A robot needs to understand where it can move, where it cannot, and how to plan paths that are not only valid but also safe and efficient. This is where costmaps come into play in ROS 2 […]
Safety in Human–Robot Interaction: Speed and Separation Monitoring with ROS 2
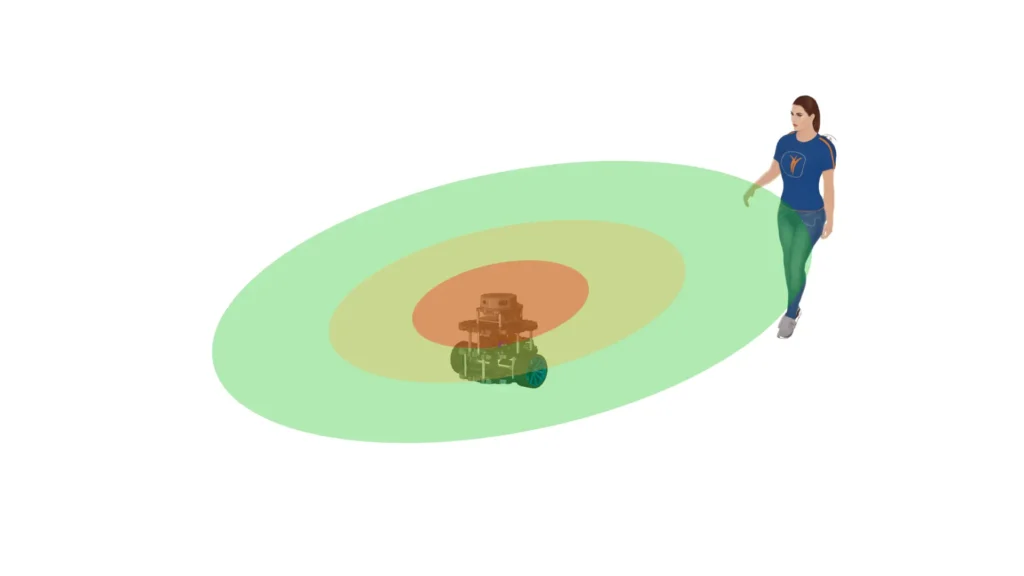
When robots and humans share the same workspace, functional safety becomes a first-class requirement. A collaborative robot must be able to adapt its motion according to the level of risk in the environment, slowing down or stopping entirely when a person comes too close.Unlike traditional setups with cages or physical barriers, this approach relies on […]
Integrating a 2D LiDAR into Your ROS 2 Robot Model

One of the key elements that enables a mobile robot to navigate autonomously is its ability to perceive the surrounding environment.Among the most widespread and reliable sensors used in robotics is the 2D LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging). This device has revolutionized mobile robotics thanks to its accuracy and the ease with which it can […]
How Robots Understand Their Environment: Maps and Localization with ROS 2
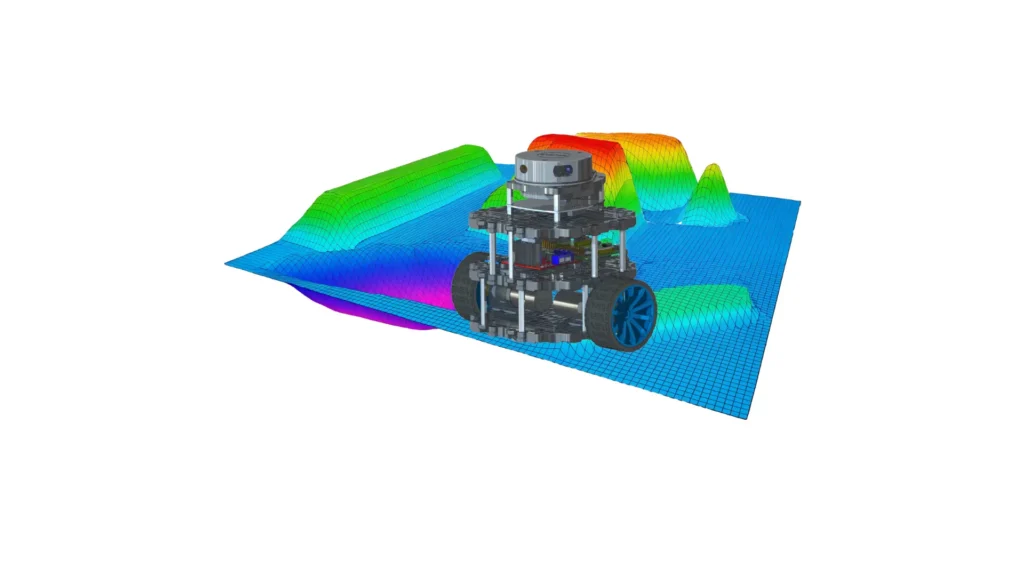
To ensure autonomous navigation capabilities, a robot must be equipped with both a localization mechanism and a representation of the environment (map).Odometry alone, based on wheel rotation measurements, is not sufficient, as it introduces cumulative errors that increase over time.Therefore, a map is required to serve as an external reference, enabling the correction of these […]
